Mood Disorders
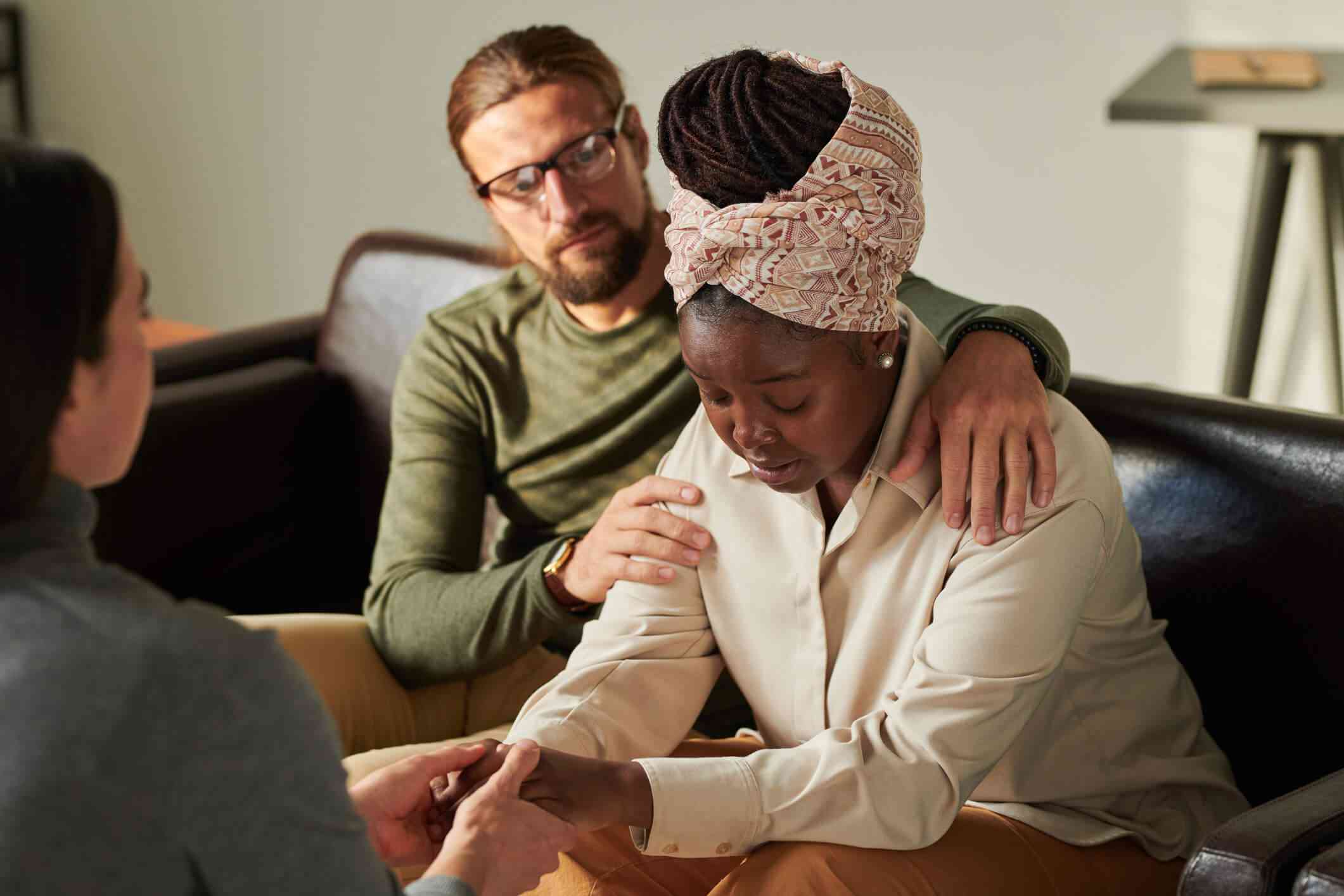
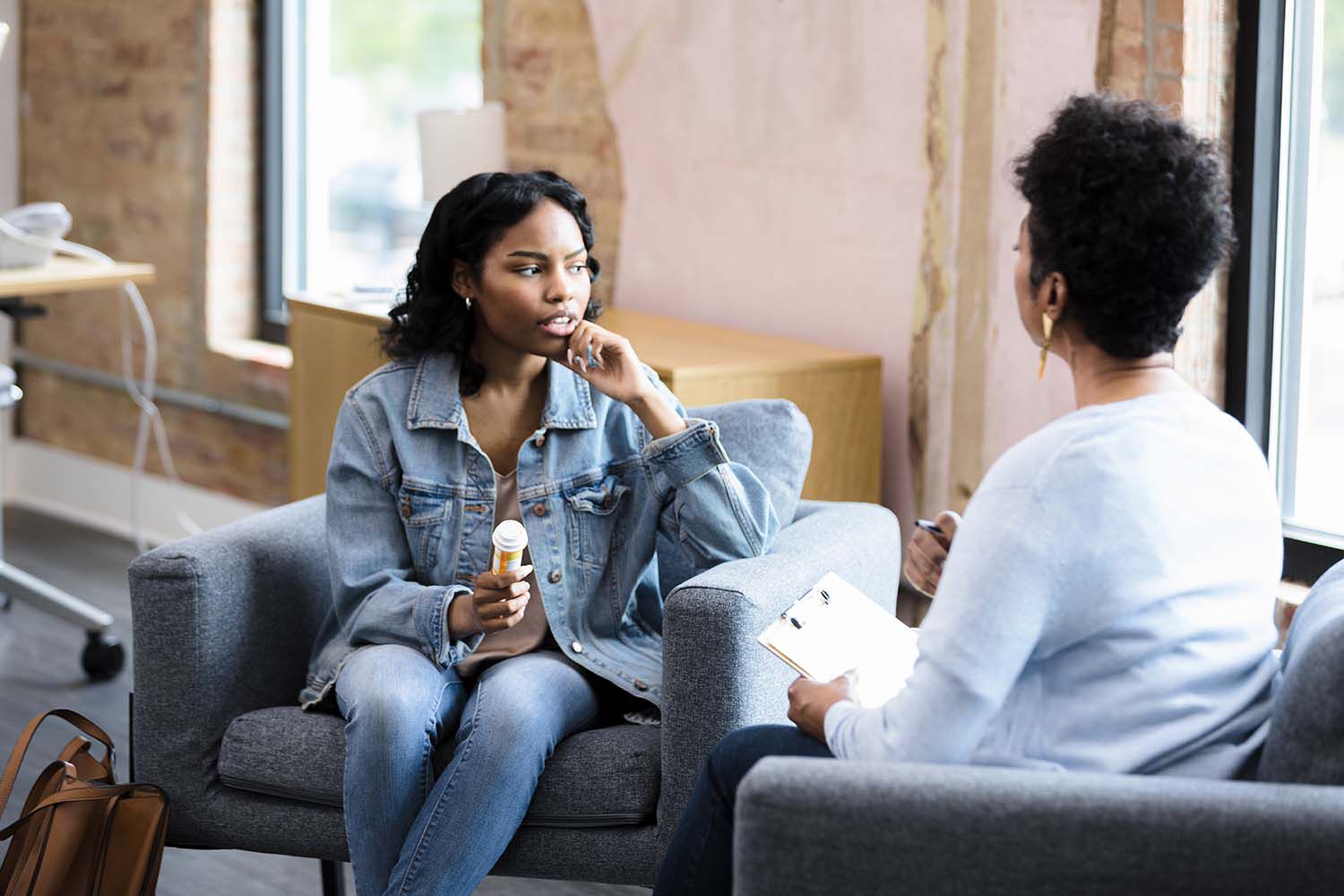
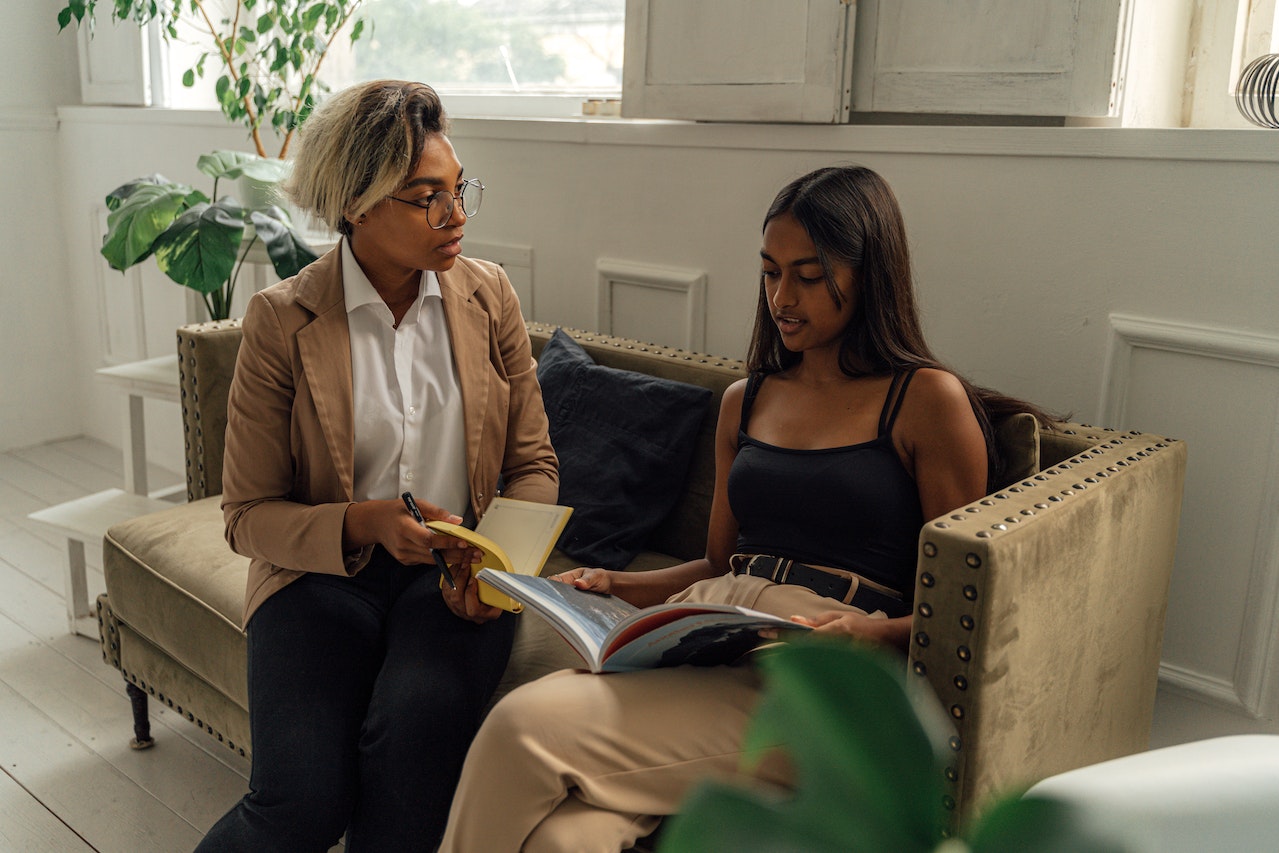
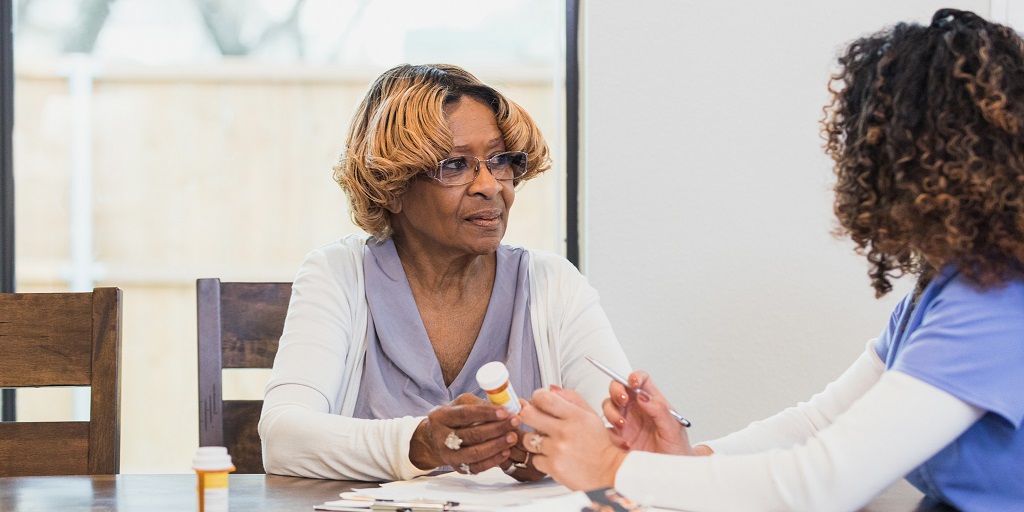
Mood disorders services in the medical field focus on the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of conditions that affect an individual’s mood. Mood disorders include conditions such as major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia). Healthcare professionals, including psychiatrists, psychologists, and primary care physicians, conduct thorough assessments to diagnose mood disorders. This involves evaluating symptoms, considering the duration and impact on daily functioning, and ruling out other medical conditions. Medication management is often a crucial component of treating mood disorders. Antidepressants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotics may be prescribed, depending on the specific diagnosis and symptoms. Regular monitoring and adjustments are made to optimize medication effectiveness. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy, and psychodynamic therapy, is commonly used to treat mood disorders. Therapy helps individuals explore and address underlying issues, develop coping strategies, and improve mood regulation. It’s important to note that treatment plans for mood disorders are highly individualized, and what works for one person may differ from another. Collaborative care involving healthcare providers, therapists, and support systems contributes to successful outcomes in the management of mood disorders. Early intervention and a combination of therapeutic modalities often yield the best results.